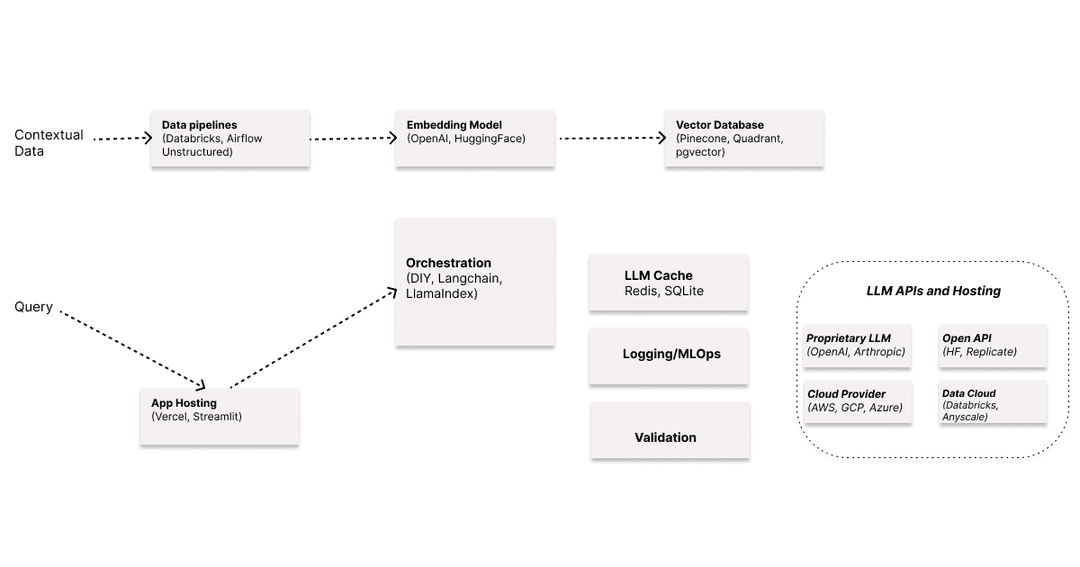
Mastering LangChain - Building Production-Ready LLM Applications LangChain has emerged as the leading framework for building applications powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). Whether you're creating chatbots, document analysis systems, or complex AI agents, LangChain provides the tools and abstractions you need to build production-ready applications.
What is LangChain?
LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by language models. It provides a standardized interface for chains, agents, memory systems, and integrations with various LLM providers and data sources.
Core Philosophy
LangChain is built on several key principles:
Composability : Build complex applications from simple, reusable componentsStandardization : Consistent interfaces across different LLMs and toolsObservability : Built-in monitoring and debugging capabilitiesProduction-Ready : Tools and patterns for deploying at scale
Core Components of LangChain
1. Models and Prompts
LangChain supports multiple LLM providers with a unified interface:
1 from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
2 from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
3 from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
4
5 # Initialize models
6 openai_model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4")
7 anthropic_model = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-sonnet-20240229")
8
9 # Create reusable prompt templates
10 prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
11 ("system", "You are a helpful AI assistant specialized in {domain}."),
12 ("human", "{input}")
13 ])
14
15 # Use with any model
16 chain = prompt | openai_model
17 response = chain.invoke({
18 "domain": "software engineering",
19 "input": "Explain microservices architecture"
20 })
21
2. Chains - Composing LLM Operations
Chains allow you to combine multiple operations into a single workflow:
1 from langchain.chains import LLMChain, SequentialChain
2 from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
3
4 # Simple chain
5 summary_template = PromptTemplate(
6 input_variables=["text"],
7 template="Summarize the following text:\n\n{text}\n\nSummary:"
8 )
9 summary_chain = LLMChain(llm=openai_model, prompt=summary_template)
10
11 # Sequential chain - multi-step processing
12 translate_template = PromptTemplate(
13 input_variables=["summary"],
14 template="Translate the following to Spanish:\n\n{summary}"
15 )
16 translate_chain = LLMChain(llm=openai_model, prompt=translate_template)
17
18 combined_chain = SequentialChain(
19 chains=[summary_chain, translate_chain],
20 input_variables=["text"],
21 output_variables=["summary", "translation"]
22 )
23
24 result = combined_chain.invoke({
25 "text": "Long article about AI..."
26 })
27
3. Agents - Dynamic Action Selection
Agents can use tools and make decisions about which actions to take:
1 from langchain.agents import create_react_agent, AgentExecutor
2 from langchain.tools import Tool
3 from langchain import hub
4
5 # Define tools
6 def search_database(query: str) -> str:
7 """Search the internal database"""
8 # Implementation
9 return f"Database results for: {query}"
10
11 def calculate(expression: str) -> str:
12 """Perform mathematical calculations"""
13 try:
14 return str(eval(expression))
15 except:
16 return "Invalid expression"
17
18 tools = [
19 Tool(
20 name="DatabaseSearch",
21 func=search_database,
22 description="Search the internal database for information"
23 ),
24 Tool(
25 name="Calculator",
26 func=calculate,
27 description="Perform mathematical calculations"
28 )
29 ]
30
31 # Create agent
32 prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/react")
33 agent = create_react_agent(openai_model, tools, prompt)
34 agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
35 agent=agent,
36 tools=tools,
37 verbose=True,
38 max_iterations=5
39 )
40
41 # Use agent
42 response = agent_executor.invoke({
43 "input": "Find the revenue for Q4 and calculate the growth percentage"
44 })
45
4. Memory Management
LangChain provides multiple memory types for maintaining conversation context:
1 from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory, ConversationSummaryMemory
2 from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
3
4 # Buffer memory - stores all messages
5 buffer_memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
6
7 # Summary memory - summarizes old conversations
8 summary_memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=openai_model)
9
10 # Conversation chain with memory
11 conversation = ConversationChain(
12 llm=openai_model,
13 memory=buffer_memory,
14 verbose=True
15 )
16
17 conversation.invoke({"input": "Hi, I'm working on a Python project"})
18 conversation.invoke({"input": "What was I just talking about?"})
19 # Memory maintains context across calls
20
Advanced LangChain Patterns
Document Loading and Processing
1 from langchain_community.document_loaders import (
2 DirectoryLoader,
3 PDFLoader,
4 UnstructuredMarkdownLoader
5 )
6 from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
7 from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
8 from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
9
10 # Load documents
11 loader = DirectoryLoader(
12 './docs',
13 glob="**/*.md",
14 loader_cls=UnstructuredMarkdownLoader
15 )
16 documents = loader.load()
17
18 # Split into chunks
19 text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
20 chunk_size=1000,
21 chunk_overlap=200,
22 length_function=len
23 )
24 chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
25
26 # Create vector store
27 embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
28 vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
29 documents=chunks,
30 embedding=embeddings,
31 persist_directory="./chroma_db"
32 )
33
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
1 from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
2 from langchain.retrievers import ContextualCompressionRetriever
3 from langchain.retrievers.document_compressors import LLMChainExtractor
4
5 # Basic RAG
6 qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
7 llm=openai_model,
8 chain_type="stuff",
9 retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 4})
10 )
11
12 # Advanced RAG with compression
13 compressor = LLMChainExtractor.from_llm(openai_model)
14 compression_retriever = ContextualCompressionRetriever(
15 base_compressor=compressor,
16 base_retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever()
17 )
18
19 compressed_qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
20 llm=openai_model,
21 retriever=compression_retriever
22 )
23
24 answer = compressed_qa.invoke({
25 "query": "What are the main features of the product?"
26 })
27
Custom Chains for Complex Workflows
1 from langchain.chains.base import Chain
2 from typing import Dict, Any
3
4 class CustomAnalysisChain(Chain):
5 """Custom chain for document analysis"""
6
7 llm: Any
8 vectorstore: Any
9
10 @property
11 def input_keys(self) -> list[str]:
12 return ["document", "analysis_type"]
13
14 @property
15 def output_keys(self) -> list[str]:
16 return ["analysis", "recommendations"]
17
18 def _call(self, inputs: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
19 document = inputs["document"]
20 analysis_type = inputs["analysis_type"]
21
22 # Custom processing logic
23 relevant_docs = self.vectorstore.similarity_search(
24 document,
25 k=3
26 )
27
28 # Perform analysis
29 analysis_prompt = f"""
30 Analyze the following document for {analysis_type}:
31 {document}
32
33 Context from similar documents:
34 {relevant_docs}
35 """
36
37 analysis = self.llm.invoke(analysis_prompt)
38
39 # Generate recommendations
40 rec_prompt = f"""
41 Based on this analysis, provide recommendations:
42 {analysis}
43 """
44
45 recommendations = self.llm.invoke(rec_prompt)
46
47 return {
48 "analysis": analysis,
49 "recommendations": recommendations
50 }
51
52 # Use custom chain
53 custom_chain = CustomAnalysisChain(
54 llm=openai_model,
55 vectorstore=vectorstore
56 )
57
58 result = custom_chain.invoke({
59 "document": "Product specification...",
60 "analysis_type": "security vulnerabilities"
61 })
62
LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
LCEL provides a declarative way to compose chains:
1 from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
2 from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
3
4 # Simple LCEL chain
5 chain = (
6 {"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
7 | prompt
8 | openai_model
9 | StrOutputParser()
10 )
11
12 result = chain.invoke("What is the pricing model?")
13
14 # Parallel execution
15 from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableParallel
16
17 chain = RunnableParallel({
18 "summary": summary_chain,
19 "sentiment": sentiment_chain,
20 "keywords": keyword_chain
21 })
22
23 results = chain.invoke({"text": "Article content..."})
24
Production Deployment Strategies
1. Caching for Performance
1 from langchain.cache import InMemoryCache, RedisCache
2 from langchain.globals import set_llm_cache
3 import redis
4
5 # In-memory cache for development
6 set_llm_cache(InMemoryCache())
7
8 # Redis cache for production
9 redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379)
10 set_llm_cache(RedisCache(redis_client))
11
12 # Cached calls are much faster
13 llm.invoke("What is AI?") # Slow - makes API call
14 llm.invoke("What is AI?") # Fast - returns cached result
15
2. Error Handling and Retries
1 from langchain.chains import LLMChain
2 from tenacity import retry, stop_after_attempt, wait_exponential
3
4 class RobustLLMChain:
5 def __init__(self, chain: LLMChain):
6 self.chain = chain
7
8 @retry(
9 stop=stop_after_attempt(3),
10 wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=1, min=4, max=10)
11 )
12 def invoke_with_retry(self, inputs: dict) -> str:
13 try:
14 return self.chain.invoke(inputs)
15 except Exception as e:
16 print(f"Error occurred: {e}")
17 raise
18
19 robust_chain = RobustLLMChain(summary_chain)
20 result = robust_chain.invoke_with_retry({"text": "Content..."})
21
3. Monitoring and Observability
1 from langchain.callbacks import StdOutCallbackHandler
2 from langsmith import Client
3
4 # LangSmith integration for monitoring
5 import os
6 os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
7 os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = "your-api-key"
8 os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "production-app"
9
10 # Custom callback for logging
11 class MetricsCallback(StdOutCallbackHandler):
12 def on_llm_start(self, *args, **kwargs):
13 # Log start time, tokens, etc.
14 pass
15
16 def on_llm_end(self, *args, **kwargs):
17 # Log completion, calculate costs
18 pass
19
20 chain = prompt | openai_model
21 result = chain.invoke(
22 {"input": "Query"},
23 config={"callbacks": [MetricsCallback()]}
24 )
25
4. Streaming Responses
1 from langchain.callbacks.streaming_stdout import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
2
3 # Streaming for real-time output
4 streaming_llm = ChatOpenAI(
5 model="gpt-4",
6 streaming=True,
7 callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()]
8 )
9
10 chain = prompt | streaming_llm
11
12 # Streams output token by token
13 for chunk in chain.stream({"input": "Write a long essay"}):
14 print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
15
Best Practices
1. Prompt Engineering with LangChain
1 from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplate
2
3 # Few-shot learning
4 examples = [
5 {"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},
6 {"input": "tall", "output": "short"},
7 ]
8
9 example_prompt = PromptTemplate(
10 input_variables=["input", "output"],
11 template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}"
12 )
13
14 few_shot_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
15 examples=examples,
16 example_prompt=example_prompt,
17 prefix="Give the opposite of each word:",
18 suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",
19 input_variables=["adjective"]
20 )
21
22 chain = few_shot_prompt | openai_model
23
2. Cost Management
1 from langchain.callbacks import get_openai_callback
2
3 with get_openai_callback() as cb:
4 result = chain.invoke({"input": "Query"})
5 print(f"Total Tokens: {cb.total_tokens}")
6 print(f"Prompt Tokens: {cb.prompt_tokens}")
7 print(f"Completion Tokens: {cb.completion_tokens}")
8 print(f"Total Cost (USD): ${cb.total_cost}")
9
3. Testing LangChain Applications
1 import pytest
2 from langchain.llms.fake import FakeListLLM
3
4 def test_chain():
5 # Use fake LLM for testing
6 fake_llm = FakeListLLM(
7 responses=["Expected response 1", "Expected response 2"]
8 )
9
10 chain = prompt | fake_llm
11 result = chain.invoke({"input": "test"})
12
13 assert "Expected" in result
14
Real-World Use Cases
Customer Support Automation
1 support_chain = (
2 {
3 "context": support_docs_retriever,
4 "history": lambda x: x["conversation_history"],
5 "question": lambda x: x["question"]
6 }
7 | support_prompt
8 | openai_model
9 | StrOutputParser()
10 )
11
Document Analysis Pipeline
1 analysis_pipeline = (
2 document_loader
3 | text_splitter
4 | embeddings
5 | vectorstore
6 | retrieval_qa
7 )
8
Code Generation Assistant
1 code_chain = (
2 {"language": RunnablePassthrough(), "task": RunnablePassthrough()}
3 | code_prompt
4 | openai_model
5 | code_parser
6 | syntax_validator
7 )
8
Conclusion
LangChain provides a comprehensive framework for building LLM applications, from simple chains to complex multi-agent systems. By leveraging its composable architecture, you can:
Build production-ready applications faster
Maintain consistency across different LLM providers
Implement complex workflows with reusable components
Monitor and optimize performance at scale
Whether you're building chatbots, document analysis systems, or intelligent agents, LangChain provides the tools and patterns you need to succeed.
The framework continues to evolve with new features, better abstractions, and improved performance. Stay engaged with the community, experiment with new patterns, and build the next generation of AI-powered applications.
Ready to build with LangChain? Start with simple chains, experiment with agents, and gradually build more complex systems. The journey to mastering LangChain is iterative - learn, build, and iterate.